Tutorial: Implementation of Siamese Network with Caffe, Theano, PyTorch, Tensorflow
Updated on 2018-07-23 14:33:23
1. caffe version:
If you want to try this network, just do as the offical document said, like the following codes:
1 ---
2 title: Siamese Network Tutorial
3 description: Train and test a siamese network on MNIST data.
4 category: example
5 include_in_docs: true
6 layout: default
7 priority: 100
8 ---
9
10 # Siamese Network Training with Caffe
11 This example shows how you can use weight sharing and a contrastive loss
12 function to learn a model using a siamese network in Caffe.
13
14 We will assume that you have caffe successfully compiled. If not, please refer
15 to the [Installation page](../../installation.html). This example builds on the
16 [MNIST tutorial](mnist.html) so it would be a good idea to read that before
17 continuing.
18
19 *The guide specifies all paths and assumes all commands are executed from the
20 root caffe directory*
21
22 ## Prepare Datasets
23
24 You will first need to download and convert the data from the MNIST
25 website. To do this, simply run the following commands:
26
27 ./data/mnist/get_mnist.sh
28 ./examples/siamese/create_mnist_siamese.sh
29
30 After running the script there should be two datasets,
31 `./examples/siamese/mnist_siamese_train_leveldb`, and
32 `./examples/siamese/mnist_siamese_test_leveldb`.
33
34 ## The Model
35 First, we will define the model that we want to train using the siamese network.
36 We will use the convolutional net defined in
37 `./examples/siamese/mnist_siamese.prototxt`. This model is almost
38 exactly the same as the [LeNet model](mnist.html), the only difference is that
39 we have replaced the top layers that produced probabilities over the 10 digit
40 classes with a linear "feature" layer that produces a 2 dimensional vector.
41
42 layer {
43 name: "feat"
44 type: "InnerProduct"
45 bottom: "ip2"
46 top: "feat"
47 param {
48 name: "feat_w"
49 lr_mult: 1
50 }
51 param {
52 name: "feat_b"
53 lr_mult: 2
54 }
55 inner_product_param {
56 num_output: 2
57 }
58 }
59
60 ## Define the Siamese Network
61
62 In this section we will define the siamese network used for training. The
63 resulting network is defined in
64 `./examples/siamese/mnist_siamese_train_test.prototxt`.
65
66 ### Reading in the Pair Data
67
68 We start with a data layer that reads from the LevelDB database we created
69 earlier. Each entry in this database contains the image data for a pair of
70 images (`pair_data`) and a binary label saying if they belong to the same class
71 or different classes (`sim`).
72
73 layer {
74 name: "pair_data"
75 type: "Data"
76 top: "pair_data"
77 top: "sim"
78 include { phase: TRAIN }
79 transform_param {
80 scale: 0.00390625
81 }
82 data_param {
83 source: "examples/siamese/mnist_siamese_train_leveldb"
84 batch_size: 64
85 }
86 }
87
88 In order to pack a pair of images into the same blob in the database we pack one
89 image per channel. We want to be able to work with these two images separately,
90 so we add a slice layer after the data layer. This takes the `pair_data` and
91 slices it along the channel dimension so that we have a single image in `data`
92 and its paired image in `data_p.`
93
94 layer {
95 name: "slice_pair"
96 type: "Slice"
97 bottom: "pair_data"
98 top: "data"
99 top: "data_p"
100 slice_param {
101 slice_dim: 1
102 slice_point: 1
103 }
104 }
105
106 ### Building the First Side of the Siamese Net
107
108 Now we can specify the first side of the siamese net. This side operates on
109 `data` and produces `feat`. Starting from the net in
110 `./examples/siamese/mnist_siamese.prototxt` we add default weight fillers. Then
111 we name the parameters of the convolutional and inner product layers. Naming the
112 parameters allows Caffe to share the parameters between layers on both sides of
113 the siamese net. In the definition this looks like:
114
115 ...
116 param { name: "conv1_w" ... }
117 param { name: "conv1_b" ... }
118 ...
119 param { name: "conv2_w" ... }
120 param { name: "conv2_b" ... }
121 ...
122 param { name: "ip1_w" ... }
123 param { name: "ip1_b" ... }
124 ...
125 param { name: "ip2_w" ... }
126 param { name: "ip2_b" ... }
127 ...
128
129 ### Building the Second Side of the Siamese Net
130
131 Now we need to create the second path that operates on `data_p` and produces
132 `feat_p`. This path is exactly the same as the first. So we can just copy and
133 paste it. Then we change the name of each layer, input, and output by appending
134 `_p` to differentiate the "paired" layers from the originals.
135
136 ### Adding the Contrastive Loss Function
137
138 To train the network we will optimize a contrastive loss function proposed in:
139 Raia Hadsell, Sumit Chopra, and Yann LeCun "Dimensionality Reduction by Learning
140 an Invariant Mapping". This loss function encourages matching pairs to be close
141 together in feature space while pushing non-matching pairs apart. This cost
142 function is implemented with the `CONTRASTIVE_LOSS` layer:
143
144 layer {
145 name: "loss"
146 type: "ContrastiveLoss"
147 contrastive_loss_param {
148 margin: 1.0
149 }
150 bottom: "feat"
151 bottom: "feat_p"
152 bottom: "sim"
153 top: "loss"
154 }
155
156 ## Define the Solver
157
158 Nothing special needs to be done to the solver besides pointing it at the
159 correct model file. The solver is defined in
160 `./examples/siamese/mnist_siamese_solver.prototxt`.
161
162 ## Training and Testing the Model
163
164 Training the model is simple after you have written the network definition
165 protobuf and solver protobuf files. Simply run
166 `./examples/siamese/train_mnist_siamese.sh`:
167
168 ./examples/siamese/train_mnist_siamese.sh
169
170 # Plotting the results
171
172 First, we can draw the model and siamese networks by running the following
173 commands that draw the DAGs defined in the .prototxt files:
174
175 ./python/draw_net.py \
176 ./examples/siamese/mnist_siamese.prototxt \
177 ./examples/siamese/mnist_siamese.png
178
179 ./python/draw_net.py \
180 ./examples/siamese/mnist_siamese_train_test.prototxt \
181 ./examples/siamese/mnist_siamese_train_test.png
182
183 Second, we can load the learned model and plot the features using the iPython
184 notebook:
185
186 ipython notebook ./examples/siamese/mnist_siamese.ipynb

If you want to shown the neural network in a image. first, you should install the following softwares:
1. sudo apt-get install graphviz
2. sudo pip install pydot2
then, you can draw the following graph using tool provided by python files.
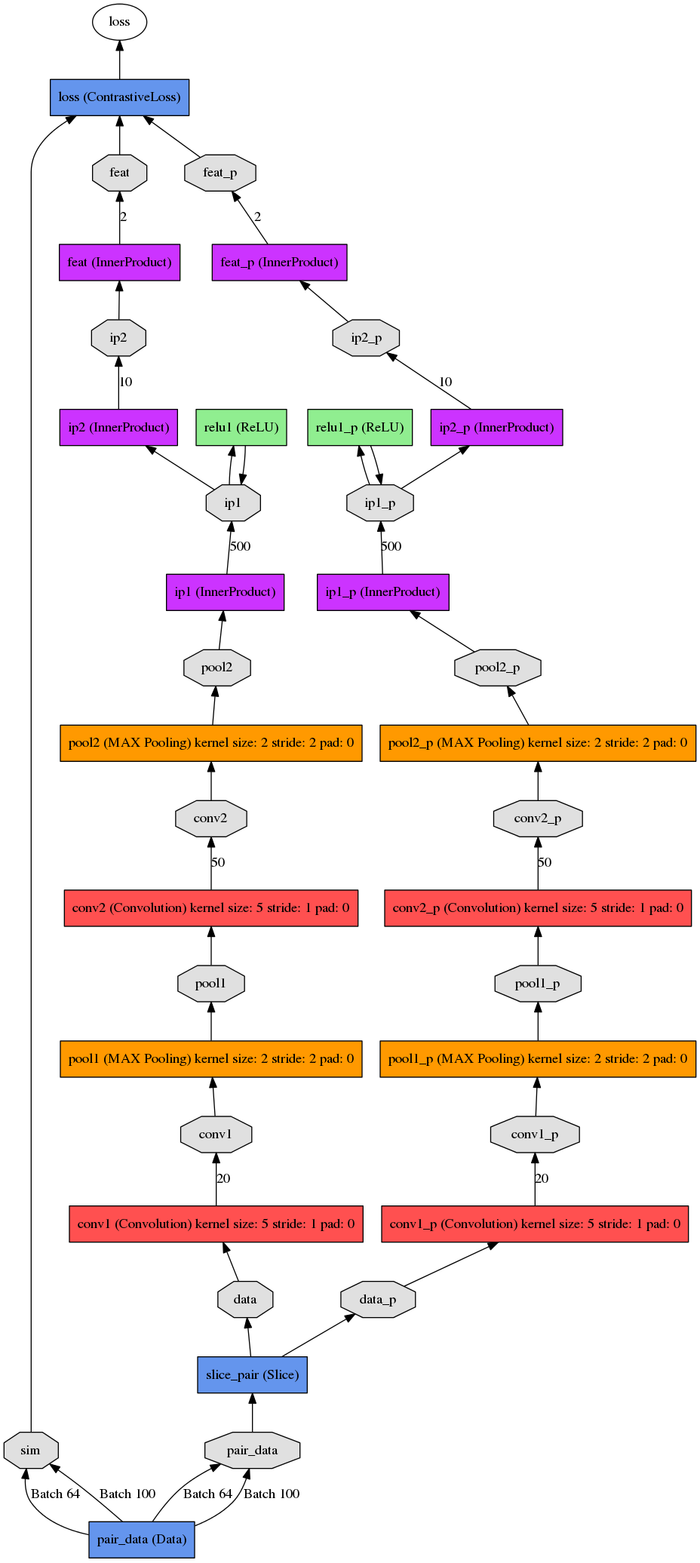
If you want to know how to implement this on your own data. You should:
1. Preparing your data:
==>> positive and negative image pairs and corresponding label (1 and -1).
2. Convert the files into lmdb files
3. then just do as above mentioned.
==>> But I am still feel confused about how to deal with this whole process.
Will fill with this part later.
2. Siamese Lasagne Theano version :
1 # Run on GPU: THEANO_FLAGS=mode=FAST_RUN,device=gpu,floatX=float32 python mnist_siamese_graph.py
2 from __future__ import print_function
3
4 import sys
5 import os
6 import time
7 import numpy as np
8 import theano
9 import theano.tensor as T
10 import lasagne
11 import utils
12 from progressbar import AnimatedMarker, Bar, BouncingBar, Counter, ETA, \
13 FileTransferSpeed, FormatLabel, Percentage, \
14 ProgressBar, ReverseBar, RotatingMarker, \
15 SimpleProgress, Timer
16 import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
17 from matplotlib import gridspec
18 import cPickle as pickle
19 import time
20 from sklearn import metrics
21 from scipy import interpolate
22 from lasagne.regularization import regularize_layer_params_weighted, l2, l1
23 from lasagne.regularization import regularize_layer_params
24
25 NUM_EPOCHS = 40
26 BATCH_SIZE = 100
27 LEARNING_RATE = 0.001
28 MOMENTUM = 0.9
29
30 # def build_cnn(input_var=None):
31 # net = lasagne.layers.InputLayer(shape=(None, 1, 64, 64),
32 # input_var=input_var)
33 # cnn1 = lasagne.layers.Conv2DLayer(
34 # net, num_filters=96, filter_size=(7, 7),
35 # nOnlinearity=lasagne.nonlinearities.rectify,
36 # W=lasagne.init.GlorotNormal())
37 # pool1 = lasagne.layers.MaxPool2DLayer(cnn1, pool_size=(2, 2))
38 # cnn2 = lasagne.layers.Conv2DLayer(
39 # pool1, num_filters=64, filter_size=(6, 6),
40 # nOnlinearity=lasagne.nonlinearities.rectify,
41 # W=lasagne.init.GlorotNormal())
42 # fc1 = lasagne.layers.DenseLayer(cnn2, num_units=128)
43 # # network = lasagne.layers.FlattenLayer(fc1)
44 # return fc1
45
46 def build_cnn(input_var=None):
47 net = lasagne.layers.InputLayer(shape=(None, 1, 64, 64),
48 input_var=input_var)
49 cnn1 = lasagne.layers.Conv2DLayer(
50 net, num_filters=96, filter_size=(7, 7),
51 nOnlinearity=lasagne.nonlinearities.rectify,
52 stride = (3,3),
53 W=lasagne.init.GlorotNormal())
54 pool1 = lasagne.layers.MaxPool2DLayer(cnn1, pool_size=(2, 2))
55 cnn2 = lasagne.layers.Conv2DLayer(
56 pool1, num_filters=192, filter_size=(5, 5),
57 nOnlinearity=lasagne.nonlinearities.rectify,
58 W=lasagne.init.GlorotNormal())
59 pool2 = lasagne.layers.MaxPool2DLayer(cnn2, pool_size=(2, 2))
60 cnn3 = lasagne.layers.Conv2DLayer(
61 pool2, num_filters=256, filter_size=(3, 3),
62 nOnlinearity=lasagne.nonlinearities.rectify,
63 W=lasagne.init.GlorotNormal())
64 # fc1 = lasagne.layers.DenseLayer(cnn2, num_units=128)
65 network = lasagne.layers.FlattenLayer(cnn3)
66 return network
67
68 def init_data(train,test):
69 dtrain = utils.load_brown_dataset("/home/vassilis/Datasets/"+train+"/")
70 dtest = utils.load_brown_dataset("/home/vassilis/Datasets/"+test+"/")
71
72 dtrain['patches'] = dtrain['patches'].astype('float32')
73 dtest['patches'] = dtest['patches'].astype('float32')
74
75 dtrain['patches'] /= 255
76 dtest['patches'] /= 255
77
78 mu = dtrain['patches'].mean()
79 dtrain['patches'] = dtrain['patches'] - mu
80 dtest['patches'] = dtest['patches'] - mu
81 return dtrain,dtest
82
83 def eval_test(net,d):
84 bs = 100
85 pb = np.array_split(d['patches'],bs)
86 descrs = []
87 for i,minib in enumerate(pb):
88 dd = lasagne.layers.get_output(net,minib).eval()
89 descrs.append(dd)
90
91 descrs = np.vstack(descrs)
92 dists = np.zeros(100000,)
93 lbls = np.zeros(100000,)
94
95 for i in range(100000):
96 idx1 = d['testgt'][i][0]
97 idx2 = d['testgt'][i][1]
98 lbl = d['testgt'][i][2]
99 dists[i] = np.linalg.norm(descrs[idx1]-descrs[idx2])
100 lbls[i] = lbl
101 #print(dists[i],lbls[i])
102 fpr, tpr, thresholds = metrics.roc_curve(lbls, -dists, pos_label=1)
103 f = interpolate.interp1d(tpr, fpr)
104 fpr95 = f(0.95)
105 print('fpr95-> '+str(fpr95))
106
107 def main(num_epochs=NUM_EPOCHS):
108 widgets = ['Mini-batch training: ', Percentage(), ' ', Bar(),
109 ' ', ETA(), ' ']
110 print("> Loading data...")
111 dtrain,dtest = init_data('liberty','notredame')
112 net = build_cnn()
113
114 dtr = utils.gen_pairs(dtrain,1200000)
115 ntr = dtr.shape[0]
116
117 X = T.tensor4()
118 y = T.ivector()
119 a = lasagne.layers.get_output(net,X)
120
121 fx1 = a[1::2, :]
122 fx2 = a[::2, :]
123 d = T.sum(( fx1- fx2)**2, -1)
124
125 l2_penalty = regularize_layer_params(net, l2) * 1e-3
126
127 loss = T.mean(y * d +
128 (1 - y) * T.maximum(0, 1 - d))+l2_penalty
129
130 all_params = lasagne.layers.get_all_params(net)
131 updates = lasagne.updates.nesterov_momentum(
132 loss, all_params, LEARNING_RATE, MOMENTUM)
133
134 trainf = theano.function([X, y], loss,updates=updates)
135
136 num_batches = ntr // BATCH_SIZE
137 print(num_batches)
138 print("> Done loading data...")
139 print("> Started learning with "+str(num_batches)+" batches")
140
141 shuf = np.random.permutation(ntr)
142
143 X_tr = np.zeros((BATCH_SIZE*2,1,64,64)).astype('float32')
144 y_tr = np.zeros(BATCH_SIZE).astype('int32')
145
146 for epoch in range(NUM_EPOCHS):
147 batch_train_losses = []
148 pbar = ProgressBar(widgets=widgets, maxval=num_batches).start()
149 for k in range(num_batches):
150 sh = shuf[k*BATCH_SIZE:k*BATCH_SIZE+BATCH_SIZE]
151 pbar.update(k)
152 # fill batch here
153 for s in range(0,BATCH_SIZE*2,2):
154 # idx1 = dtrain['traingt'][sh[s/2],0]
155 # idx2 = dtrain['traingt'][sh[s/2],1]
156 # lbl = dtrain['traingt'][sh[s/2],2]
157
158 idx1 = dtr[sh[s/2]][0]
159 idx2 = dtr[sh[s/2]][1]
160 lbl = dtr[sh[s/2]][2]
161
162 X_tr[s] = dtrain['patches'][idx1]
163 X_tr[s+1] = dtrain['patches'][idx2]
164 y_tr[s/2] = lbl
165
166 batch_train_loss = trainf(X_tr,y_tr)
167 batch_train_losses.append(batch_train_loss)
168 avg_train_loss = np.mean(batch_train_losses)
169 pbar.finish()
170 print("> Epoch " + str(epoch) + ", loss: "+str(avg_train_loss))
171
172 eval_test(net,dtest)
173
174 with open('net.pickle', 'wb') as f:
175 pickle.dump(net, f, -1)
176
177 # netlayers = lasagne.layers.get_all_layers(net)
178 # print(netlayers)
179 # layer = netlayers[1]
180 # print(layer)
181 # print(layer.num_filters)
182 # W = layer.W.get_value()
183 # b = layer.b.get_value()
184 # f = [w + bb for w, bb in zip(W, b)]
185 # gs = gridspec.GridSpec(8, 12)
186 # for i in range(layer.num_filters):
187 # g = gs[i]
188 # ax = plt.subplot(g)
189 # ax.grid()
190 # ax.set_xticks([])
191 # ax.set_yticks([])
192 # ax.imshow(f[i][0])
193 # plt.show()
194
195
196 if __name__ == '__main__':
197 main(sys.argv[1])
3. Tensorflow version :
Github link: https://github.com/ywpkwon/siamese_tf_mnist
4. PyTorch Version:
Github link: https://github.com/harveyslash/Facial-Similarity-with-Siamese-Networks-in-Pytorch/blob/master/Siamese-networks-medium.ipynb

5.

 京公网安备 11010802041100号 | 京ICP备19059560号-4 | PHP1.CN 第一PHP社区 版权所有
京公网安备 11010802041100号 | 京ICP备19059560号-4 | PHP1.CN 第一PHP社区 版权所有